Digital Dynamo: Unleashing the Power of Digital Marketing
 Mastering Digital Marketing Strategies
Mastering Digital Marketing Strategies Digital Marketing utilises digital channels and tools such as the internet, mobile devices, social media and other digital means to promote brands and related goods – products and services. Unlike and beside conventional marketing, digital marketing offers a unique set of tools, initiatives and opportunities that are exclusive to the online environment.
Although in the early days of its popularity it might have been thought that digital marketing was only an online projection of traditional marketing, digital marketing is now acknowledged as an independent discipline with distinctive features and practices.
Key and characteristics aspects of digital marketing:
•Global Reach: Unlike traditional marketing, digital strategies enable businesses, including those in rural areas, to reach a global audience, breaking geographical barriers
•Performance Analytics: Online platforms and tools offer tracking and data analytics options, allowing for comprehensive assessment of strategies and campaign performance
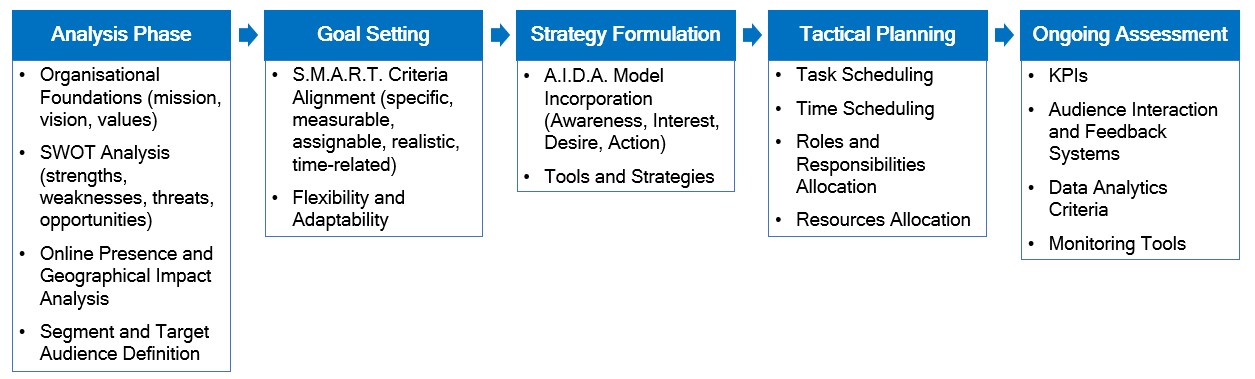
A Digital Marketing Plan represents a strategic document outlining and organisation’s objectives and the related strategies to achieve them in terms of digital marketing and communication. It encompasses roles, responsibilities, timelines and monitoring tools for an effective implementation and evaluation of digital marketing strategies.
While sharing similarities with the traditional marketing plan, a digital marketing plan distinguishes itself operationally. It enables real-time measurement and the formulation of a flexible short-term strategy, emphasising an iterative process between action and control.
This operational difference stems from the ease with which digital marketing enables continuous evaluation of strategies through the analysis of audience interactions and reactions. The direct relationship with the audience eliminates the need to wait for the results of sales of products or services, moving towards a continuous evaluation rather than an after-the-fact one.
In other words, the focus shifted…
…from final evaluation à to Ongoing Assessment
Key steps for the development of a digital marketing plan:

Introductive overview: Lead Generation serves as the key starting point for engaging with the audience in their customer journey. It initiates the process of connecting with potential customers and forms the foundation for a comprehensive digital marketing strategy. In the upcoming sections, the subsequent phases will be explored: conversion and retention.
Specifically, lead generation strategy represents the first contact with potential customers through the involvement of meticulous acquisition of their contact data and details. When well-structured, lead generation offers several advantages:
Here are effective techniques to incorporate into your lead generation strategy:
Once potential customers have been identified and engaged, the focus shifts to systematically guiding them towards desired actions, such as become leads or making a purchase (buyers). This critical phase, known as the Conversion Phase, ensures that the efforts invested in marketing and attracting prospects translate into concrete interactions and tangible outcomes, contributing to business growth and success.
To enhance conversions, a structured conversion research process is essential. This process identifies existing issues, their nature, and the rationale for addressing them.
Conversion Rate Optimisation (CRO):
In the realm of conversion optimisation, businesses refine their strategies to create a seamless journey from initial engagement to meaningful customer actions.
Customer Retention goes beyond merely keeping customers close, it is about cultivating lasting relationships to transform customers into steadfast brand advocates – a sort of brand ambassadors.
Key factors influencing customer retention:
Strategies for Customer Retention:
Focus on Microenterprises in Rural Areas:
In this context, a retained customer not only ensures repeat business but also transforms them into potential local brand ambassadors. This local influence, coupled with digital strategies like online reviews, allows rural businesses to extend their impact beyond local boundaries. Customer retention thus becomes a dual strategy, solidifying the business within the local community while leveraging the digital space to reach a wider audience through the advocacy of retained customers.
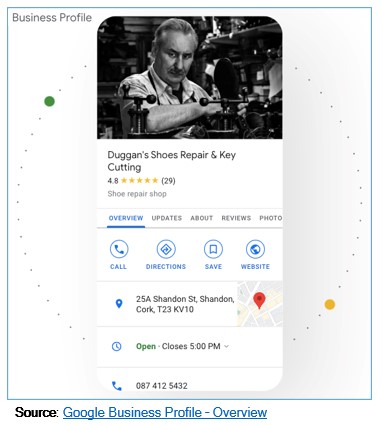
“Stand out on Google with a Business Profile”
Google Business Profile is a powerful tool for establishing and enhancing the business’ online presence. It serves as a virtual storefront, providing essential information (name, address, number, directions, photos, opening hours, website, reviews, etc.) about a business to potential consumers.
How Google Business Profile Benefits Rural Microenterprises:
 Digital Communication and Interaction
Digital Communication and InteractionDigital Communication acts as the conduit for the seamless exchange of data and information facilitated by digital technologies and platforms. This enables real-time interaction, instant messaging, video conferencing, and the seamless sharing of multimedia content across vast distances.
Critical elements of digital communication include instantaneous interaction, seamless multimedia integration, a harmonious blend of both asynchronous and synchronous communication, heightened accessibility and convenience, collaborative co-creation, meticulous data preservation and archiving, scalable reach, a global footprint, and seamless integration with other cutting-edge technologies. Together, these elements form the pillars of a robust digital communication framework.
Focus on Microenterprises in Rural Areas:
Digital communication represents a precious tool to overcome geographical barriers and foster community engagement. Microenterprises, often situated in rural settings, can utilise digital platforms to maintain connections with their local (and not) customer base.
Imagine a local artisan in a rural area using social media and digital communication to showcase their traditional craftsmanship through multimedia content. This not only preserves the cultural heritage of the community but also opens doors for global appreciation and market.
Digital communication enables microenterprises to not only stay connected locally but also expand their reach and visibility on a broader scale.
A comprehensive digital communication strategy entails careful planning for online communication, emphasising the dynamic interplay between two key elements:
An effective strategy not only allows to reach the audience but also fosters interaction with them, employing the methodology of interactive communication.
Interactive Communication, facilitated through digital tools and technology, serves as a mechanism for businesses to establish seamless and engaging connections with their audience. It involves one-on-one conversations, distinguishing itself from traditional communication by creating a feedback loop, making it exceptionally effective.
Incorporating interactive communication within the digital strategy involves implementing dynamic strategies, such as:
•Email Marketing Campaigns: Implementing personalised and targeted email campaigns to maintain regular communication and provide valuable content to the audience
Focusing on Social Media, here are key steps to guide a business on how to choose the right social media platform:
5.Determination of Social Media Strategy: Defining goals, researching competitors, developing content strategies, and implementing a monitoring and measurement system are essential to track and optimize results
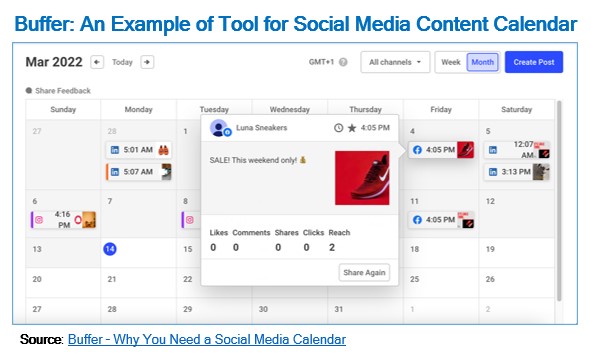
An Effective Editorial Plan serves as strategic roadmap guiding businesses toward successful digital marketing and communication. This strategic document not only defines the content to be published online but also orchestrates a cohesive and impactful narrative that resonates with the target audience. Key components are:
The integration of digital marketing and communication strategies marks the convergence of two powerful forces that, when harmonised effectively, propel a business toward success in the digital landscape. Key aspects of integration:
 Summing Up
Summing Up
This unit equips learners with a comprehensive understanding of digital marketing’s distinctive features, including global reach, personalisation, and interactive engagement. From developing strategic digital marketing plans to exploring lead generation and optimising conversions, participants gain insights into creating lasting customer relationships in the digital age. The unit concludes by showcasing the significance of a robust online presence through platforms like Google Business Profile, particularly beneficial for microenterprises in rural areas

Unit 2 delves into the dynamics of digital communication, emphasising real-time interaction, multimedia integration, and scalable reach. Learners explore interactive communication strategies, choose effective social media platforms, and craft editorial plans and content calendar for impactful digital marketing
 Test Yourself
Test YourselfDigital Marketing; Digital Marketing Plan; Lead Generation; conversion; Retention; Google Business Profile; Digital Communication; Social Media Platform; Editorial Plan; Content Calendar; Digital Marketing and Communication Strategies
Objectives:
At the end of this module, you will be able to:
DIGITAL MARKETING
- Understand the core principles and components of digital marketing
- Explore the functions of a comprehensive digital marketing plan aligned with business objective
- Implement strategies for lead generation and optimise conversion rates
DIGITAL COMMUNICATION AND INTERACTION
- Comprehend the role of digital communication in marketing and brand building
- Choose the right social media platforms and tailor strategies accordingly
- Develop and implement effective editorial plans for content strategy
Learning Outcomes:
- Recognise and articulate fundamental terms and concepts crucial for a comprehensive understanding of digital marketing, including branding, comprehensive approach, global reach, personalisation, user-friendly design, interactive engagement, and performance analytics
- Demonstrate the knowledge to develop strategic digital marketing plans by analysing organisational foundations, conducting SWOT analyses, defining target audiences, setting SMART goals, formulating effective strategies using models like AIDA, and planning tactical executions with resource considerations and ongoing assessment techniques
- Outline effective techniques for lead generation, including the creation of landing pages, streamlined forms, quality content, live interactions, advertisements, contests, reviews, and remarketing, preparing them for targeted marketing and sales efforts
- Delve into the conversion phase of the customer journey, exploring Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO) and effective customer retention strategies. The focus on microenterprises in rural areas will be highlighted, showcasing strategies that transcend geographical barriers for lasting connections
EQF
Level 4
DigiComp 2.2:
- - Communication and collaboration
- - Digital content creation
Competence(s):
- Integrating through digital technologies
- Sharing information and content through digital technologies
- Engaging in citizenship through digital technologies
- Collaborating through digital technologies
- Netiquette
- Managing digital identity
EntreComp:
- - Ideas & opportunities
- - Resources
Competence(s):
- Valuing ideas
- Self-awareness & self-efficacy
- Mobilising others






